10 Essential Things You Need to Know About Cloud Computing: Beginner to Advanced Guid
Table of Contents
Cloud computing has revolutionized how businesses, developers, and individuals manage data, run applications, and scale operations efficiently. Instead of relying on physical servers or local computers, cloud computing allows users to access computing resources over the internet—securely, flexibly, and on demand.
From start-up’s to multinational corporations, cloud computing services power websites, mobile apps, AI systems, data analytics, and enterprise software. Understanding what is cloud computing and how it works is now essential for modern technology adoption.
Basics of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing refers to delivering computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet.
Instead of buying and maintaining physical hardware, users rent resources from cloud service providers and pay for usage only.
Key characteristics of cloud computing include:
- On-demand self-service
- Broad network access
- Resource pooling
- Rapid scalability
- Measured service (pay-as-you-go)
These features make cloud computing the backbone of modern enterprise cloud solutions.
How Cloud Computing Works
Cloud computing operates through a global network of remote servers hosted in data centers. These servers handle data processing, storage, and application delivery.
Core Components
- Frontend: User devices such as browsers or mobile apps
- Backend: Servers, databases, and storage systems
- Network: Internet connectivity for remote access
- Virtualization: Layer that allows multiple virtual machines on a single server
When users request a service, cloud automation dynamically allocates resources, delivering results instantly and improving operational efficiency in healthcare, business, or enterprise settings.
Types of Cloud Computing Services
Cloud computing services are categorized based on user control and technical requirements.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Provides virtualized computing resources like servers, storage, and networking.
Examples: AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine
Use Cases: Hosting websites, disaster recovery, enterprise cloud solutions
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Provides a platform for developers to build, test, and deploy applications.
Examples: Google App Engine, Azure App Services
Use Cases: Application development, AI & ML deployment
Software as a Service (SaaS)
Delivers ready-to-use software over the internet.
Examples: Gmail, Salesforce, Dropbox
Use Cases: Business productivity, enterprise cloud solutions, remote team collaboration
Cloud Deployment Models
Cloud deployment models define where infrastructure is hosted and how organizations access it.
Main Models
- Public Cloud – Shared infrastructure by third-party providers
- Private Cloud – Dedicated infrastructure for one organization
- Hybrid Cloud – Mix of public and private cloud infrastructure
- Multi-Cloud – Use of multiple cloud service providers simultaneously
Each model supports cloud scalability, automation across the hybrid cloud, and data security in cloud.
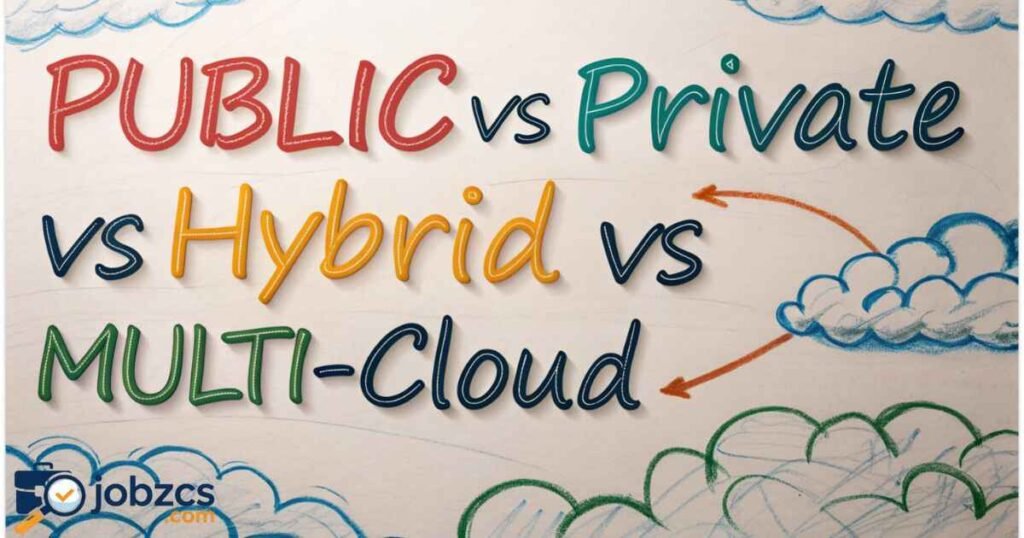
Public vs Private vs Hybrid vs Multi-Cloud
Public Cloud:
- Pros: Cost-effective, scalable
- Cons: Less control over cloud security
Private Cloud:
- Pros: High control, strong data security
- Cons: Higher costs, infrastructure management required
Hybrid Cloud:
- Pros: Flexible, meets compliance requirements
- Cons: Complex management
Multi-Cloud:
- Pros: Reduces vendor lock-in
- Cons: Requires sophisticated cloud virtualization management
Cloud Virtualization Explained
Virtualization is the backbone of cloud computing. It allows multiple virtual machines to run on one physical server, increasing cloud infrastructure efficiency.
Key Technologies
- Virtual Machines (VMs)
- Containers (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Hypervisors
Virtualization enhances operational efficiency in healthcare, enterprise cloud solutions, and automation across hybrid cloud environments.
Cloud Infrastructure and Building Clouds
Cloud infrastructure consists of:
- Compute resources
- Storage systems
- Networking components
- Data centers
Building cloud infrastructure requires redundancy, fault tolerance, and high availability to ensure scalability and data security in cloud systems.
Automation Across the Hybrid Cloud
Cloud automation allows organizations to deploy and scale services faster while reducing human error.
Key Automation Tools
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC)
- Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
- Auto-scaling systems
- Orchestration platforms
Automation increases enterprise cloud solutions efficiency and enables proactive management of cloud resources.
Cloud Security and Compliance
Security is critical in cloud computing. Cloud security involves protecting data, applications, and infrastructure from threats.
Security Measures
- Data encryption
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Firewalls and monitoring
- Compliance certifications: ISO, GDPR, HIPAA
Cloud service providers follow a shared responsibility model, splitting security duties between the provider and the organization.

Advanced Concepts of Cloud Computing
Serverless Computing
Run applications without managing servers, focusing on business logic.
Edge Computing
Process data closer to users to reduce latency.
AI & Machine Learning in Cloud
Cloud platforms provide AI tools, enabling data analytics, automation, and predictive insights.
Top Leading Cloud Computing Companies
Major Providers
- Amazon Web Services (AWS)
- Microsoft Azure
- Google Cloud Platform (GCP)
- IBM Cloud
- Oracle Cloud
These providers dominate cloud service models, cloud deployment models, and cloud infrastructure scalability.
Choosing the Right Cloud Service Provider
Key Decision Factors
- Pricing structure
- Security and compliance
- Performance & uptime
- Support & ecosystem
- Scalability needs
Selecting the right provider improves enterprise cloud solutions, operational efficiency, and automation across hybrid cloud setups.
Benefits and Challenges of Cloud Computing
Benefits
- Cost efficiency
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Remote accessibility
- Supports digital transformation
Challenges
- Security concerns
- Downtime risks
- Vendor lock-in
- Compliance complexity
Understanding these helps organizations fully leverage cloud computing services.
Future of Cloud Computing
The future of cloud computing includes:
- AI-driven automation
- Edge and 5G integration
- Sustainable cloud infrastructure
- Increased multi-cloud adoption
- Industry-specific cloud solutions
Cloud computing will continue powering enterprise cloud solutions and digital transformation strategies globally.
Conclusion
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses, developers, and individuals manage data, applications, and digital infrastructure. By leveraging cloud service models, organizations gain scalability, cost efficiency, and operational flexibility that traditional IT systems cannot match. Whether you choose public, private, hybrid, or multi-cloud deployment models, adopting the right cloud computing services empowers you to innovate faster, reduce infrastructure overhead, and enhance enterprise cloud solutions.
As automation across hybrid cloud environments advances, AI-powered tools, virtualization, and serverless computing will continue to drive digital transformation across industries. By understanding the benefits, challenges, and best practices of cloud computing, you can make informed decisions, improve cloud security, and unlock the full potential of your IT strategy. Embrace cloud technology today to future-proof your business, boost efficiency, and stay ahead in the competitive digital landscape.
FAQs
What is cloud computing in simple words?
Cloud computing is using the internet to store data and run applications instead of relying on a local computer.
What are the main types of cloud computing?
The main types are IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS.
Is cloud computing secure?
Yes, cloud security measures like encryption, IAM, and compliance standards protect data.
What is the difference between cloud and traditional computing?
Traditional computing uses local hardware, while cloud computing relies on remote servers accessible online.
Which companies use cloud computing?
Companies like Netflix, Amazon, Google, Facebook, and Microsoft use cloud computing services extensively.

Stephen King writes about a wide range of topics, including Business & Finance, Skilled Trades, Healthcare, Technology, Remote Jobs, and Nail Care & Nail Art. He aims to provide practical tips, insights, and inspiration for both professionals and creative enthusiasts. With a focus on clarity and usefulness, Stephen helps readers navigate career growth, industry trends, and personal creativity all in one place.